BECA 235P/AE
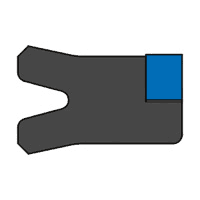


Description
The BECA 235P/AE profile is a rubber U-ring type single acting piston seal with symmetrical lips and a POM back-up ring.
Advantages
Optimised sealing effect
Excellent resistance to high temperatures depending on the type of material chosen
Good extrusion resistance
Technical data
| Temperature | -30°C/+200°C |
|---|---|
| Pressure | 25 MPa |
| Speed | 0.5 m/s |
| Medias | Mineral hydraulic oils |
Applications
Mobile machinery
Machine tools
Presses
Standard cylinders
Materials
Profiled seal
NBR 70 Shore A
NBR 85 Shore A
FKM 85 Shore A
Back-up ring
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Bronze-filled PTFE
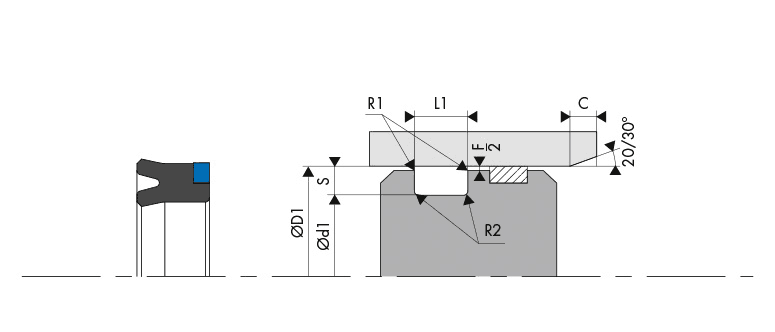
Dimensions
Materials
NBR
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is the general term for acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer. The ACN content can vary between 18% and 50%. While the acrylonitrile content is important, the resistance to oil and fuel is more so. Conversely, the elasticity and compression set are not as good. The NBR has good mechanical properties and good wear resistance. However, its resistance to atmospheric agents and the ozone is relatively low.
| Chemical resistance | Aliphatic hydrocarbons (propane, butane, petroleum, diesel fuel) Mineral oils and greases Fire-resistant fluids (HFA, HFB and HFC) Diluted acids, low-temperature alkaline and saline solutions Water (up to +100°C max) |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Fuels with high aromatic content Aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene) Chlorinated hydrocarbons (trichlorethylene) Polar solvents (ketone, acetone, acetic acid, ethylene-ester) Strong acids Glycol-based brake fluids Atmospheric and ozone agents |
| Temperature range | -30°C/+100°C -40°C / +100°C with our low-temperature NBR |
EPDM
As an Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer copolymer, EPDM is a rubber commonly used for hot water taps, cooling systems, brake systems, dishwashers and washing machines.
| Chemical resistance | Hot water and steam up to +150°C Glycol-based brake fluids (Dot 3 & 4) and silicone-based brake fluids (Dot 5) Organic and inorganic acids Cleaning agents, sodium and potassium alkalis Hydraulic fluids (HFD-R) Silicone oils and greases Polar solvents (alcohols, ketones and esters) Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Mineral oils and greases Hydrocarbons Low impermeability to gas |
| Temperature range | -45°C/+150°C |
FKM
Depending on their structure and fluorine content, the chemical resistance and resistance to the cold in fluororubbers can vary. This FKM-based rubber is very often used for high-temperature hydraulics and pneumatics, for industrial valves, injection/fuel systems, motor seals and high-vacuum systems.
| Chemical resistance | Mineral oils and greases, ASTM n°1, IRM 902 and IRM 903 oils. Fire-resistant liquids (HFD) Silicone oils and greases Mineral and vegetable oils and greases Aliphatic hydrocarbons (propane, butane, petroleum) Aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluene) Chlorinated hydrocarbons (trichlorethylene) Fuel (including high alcohol content) Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Glycol-based brake fluids Ammonia gas Organic acids with a low molecular weight (formic and acetic acids) |
| Temperature range | -20°C/+200°C -40°C / +200°C with our FKM GLT on request |
HNBR
This HNBR-based rubber is obtained through selective hydrogenation of the NBR's butadiene groups. It is commonly used for power-assisted steering and for air conditioning.
| Chemical resistance | Aliphatic hydrocarbons Mineral and vegetable oils and greases Fire-resistant fluids (HFA, HFB and HFC) Diluted acids, saline solutions and bases for operation at an average temperature Water and steam up to +150°C Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Chlorinated hydrocarbons Polar solvents (ketones, esters and ethers) Strong acids |
| Temperature range | -30°C/+150°C |
ACM
Polymers containing ethyl acrylate (or butyl acrylate) have a small amount of monomer, which is necessary for cross-linking; ACM is a material with better heat resistance than NBR. It is often used for automatic gearboxes.
| Chemical resistance | Mineral oils (motor oils, gear box oils, ATF oils) Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Glycol-based brake fluids (Dot 3 & 4) Aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons Water and steam Acids, alkalis and amines. |
| Temperature range | - 25°C to + 150°C |
VMQ
This VMQ-based rubber is very often used in fuel systems.
| Chemical resistance | Animal and vegetable oils and greases Water for operation at an average temperature Diluted saline solutions Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Superheated steam up to +120°C Chlorinated hydrocarbons with a low molecular weight (trichlorethylene) Aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluene) |
| Temperature range | -60°C/+200°C |
Polyoxymethylene - POM
Polyoxymethylene (POM or polyacetal) belongs to the thermoplastics, which have a number of advantages - strong mechanical resistance, good creep strength, high resistance to shocks, particularly at low temperatures, good wear resistance, good sliding coefficient, excellent machinability and good dielectric properties. The low water absorption coefficient, unlike polyamide (PA), also gives this material an excellent dimensional stability.
| Chemical resistance |
Aliphatic hydrocarbons (propane, butane, petroleum, diesel fuel) |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Acids |
| Temperature range | -50°C/+115°C |
Bronze-filled PTFE
PTFE is a thermoplastic polymer made of tetrafluoroethylene with exceptional properties - very low friction coefficient (adhesive friction and sliding friction are almost equal), physiologically safe for temperatures up to +200°C, excellent electrical insulation properties, and excellent chemical compatibility with the majority of fluids. On the other hand, as this material is plastic and not elastic, so it cannot easily replace rubber bases.
Between 40% and 60% of bronze is added to the PTFE as a filler. This machined material has excellent wear resistance, low creep deformation and good thermal conductivity.
Technical data
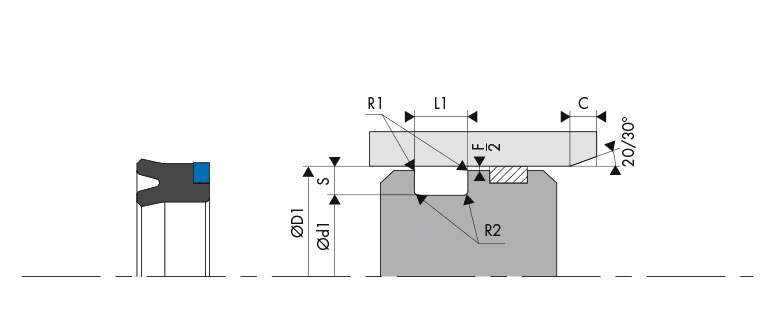
Extrusion gaps
| Pressure MPa |
Radial extrusion gap F/2 |
|---|---|
| 2.5 MPa | 0.45 |
| 5.0 MPa | 0.35 |
| 7.5 MPa | 0.30 |
| 10.0 MPa | 0.25 |
| 15.0 MPa | 0.20 |
| 25.0 MPa | 0.10 |
Surface roughness
| Roughness | Dynamic surface area | Static surface area | Groove flanks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ra | 0.1 - 0.4 µm | ≤ 1.6 µm | ≤ 3.2 µm |
| Rz | 0.63 - 2.5 µm | ≤ 6.3 µm | ≤ 10.0 µm |
| Rmax | 1.0 - 4.0 µm | ≤ 10.0 µm | ≤ 16.0 µm |
Chamfers and radius
| Radial section S |
Radius R1 |
Radius R2 |
Chamfer C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.50 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 2.00 |
| 5.00 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 2.50 |
| 7.50 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 4.00 |
| 10.00 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 5.00 |
Only on request
